29+ Alkane Functional Group Structure
Alkane Functional Group Structure. In alkene, carbon = carbon double bond is the functional group. When the carbons are not all in a straight chain, the alkane is said to be branched.

The end carbons are bonded to only one carbon, but three hydrogens. Benzene ring structure (a) that is characterized by alternating double bonds. Branched alkanes are alkanes where carbon chain is split off making one or more branch.
atoll coral reef examples antenne tnt interieur boulanger alarmed app no sound ampoule h4 led avis
Alkanes Structural Isomers 16 •Depending on the number
So we start with an alkene. The end carbons are bonded to only one carbon, but three hydrogens. Functional groups • organic molecules are often organized by structures called functional groups, which are characteristic arrangement of atoms which define many of the physical and chemical properties of a class of organic compounds. So we start with an alkene.

We'll be learning about different aspects of molecular structure, including common functional groups and conformations. Ultradur, pbt is a plastic polymer that contains an aromatic functional group. Ethers have a pair of alkyl or aromatic groups attached to a linking oxygen atom. Aromatics are cyclic strcutures that are planar, fully conjugated and that possess an odd number of electron pairs.

Branched alkanes are alkanes where carbon chain is split off making one or more branch. Identify the functional groups in the following model of arecoline, a veterinary drug used to control worms in animals. 3.2 alkanes and alkane isomers before beginning a systematic study of the different functional groups, let’s look Benzene ring structure (a) that is characterized by alternating.

Branched alkanes are alkanes where carbon chain is split off making one or more branch. Most reactions of organic compounds take place at or adjacent to a functional group.in order to establish a baseline of behavior against which these reactions may be ranked, we need to investigate the reactivity of compounds lacking any functional groups. The properties of organic molecules.

Functional groups • organic molecules are often organized by structures called functional groups, which are characteristic arrangement of atoms which define many of the physical and chemical properties of a class of organic compounds. So we start with an alkene. R refers to the rest of the compound, or the remainder of the compound, and normally we're talking about carbons.

In alkane, actually no functional group is present. The general formula of linear alkanes is c n h 2n+2. When the carbons are not all in a straight chain, the alkane is said to be branched. The general formula of branched alkanes is c n h. 26 rows name of functional group structure:
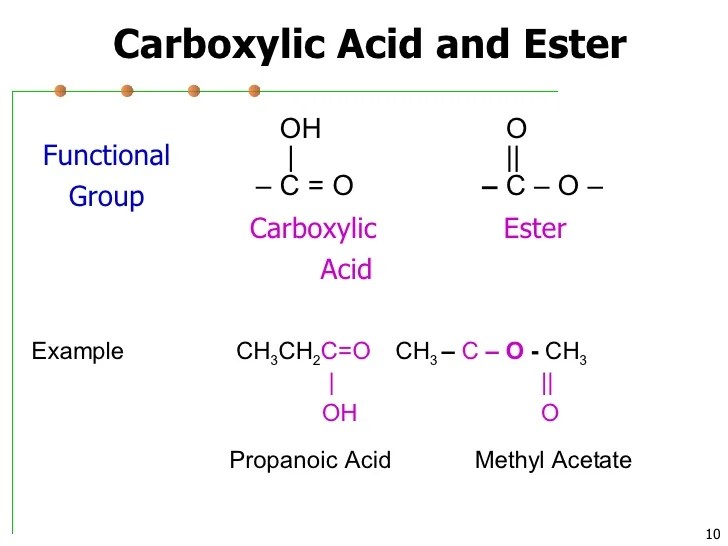
Ultradur, pbt is a plastic polymer that contains an aromatic functional group. The general formula is cnh2n+2, (alkane functional group). R refers to the rest of the compound, or the remainder of the compound, and normally we're talking about carbons and hydrogens. The general formula of branched alkanes is c n h. In alkene, carbon = carbon double bond is.

Ethers have a pair of alkyl or aromatic groups attached to a linking oxygen atom. The end carbons are bonded to only one carbon, but three hydrogens. We'll be learning about different aspects of molecular structure, including common functional groups and conformations. The properties of organic molecules depend on the structure, and knowing the names of organic compounds allow us.