21++ Alkane To Alkene To Alkyne
Alkane To Alkene To Alkyne. For example, alkynes undergo many of the typical addition reactions of alkenes. Alkenes and alkynes can be transformed into almost any other functional group you can name!
Halogenation goes via free radical mechanism and thus lot of unwanted products + other isomers can be formed. The addition of halogens in alkenes result in the making of organic salts. This gives them a general formula :
3d black hole tattoo applique murale solaire exterieur avec detecteur 20 50 house map 2 hours later spongebob gif
Cycloalkanes, Aromatic hydrocarbons, Preparation of
In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density! For example, alkynes undergo many of the typical addition reactions of alkenes. About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features press copyright contact us creators. We will review their nomenclature, and also learn about the vast possibility of reactions using alkenes and alkynes as starting materials.

In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density! Alkynes are unsaturated carbon that shares a triple bond at the carbon site. The alkanes are also called as paraffins. Methane gas is the first member of the homologous series of alkanes. The double bond is broken and each carbon.

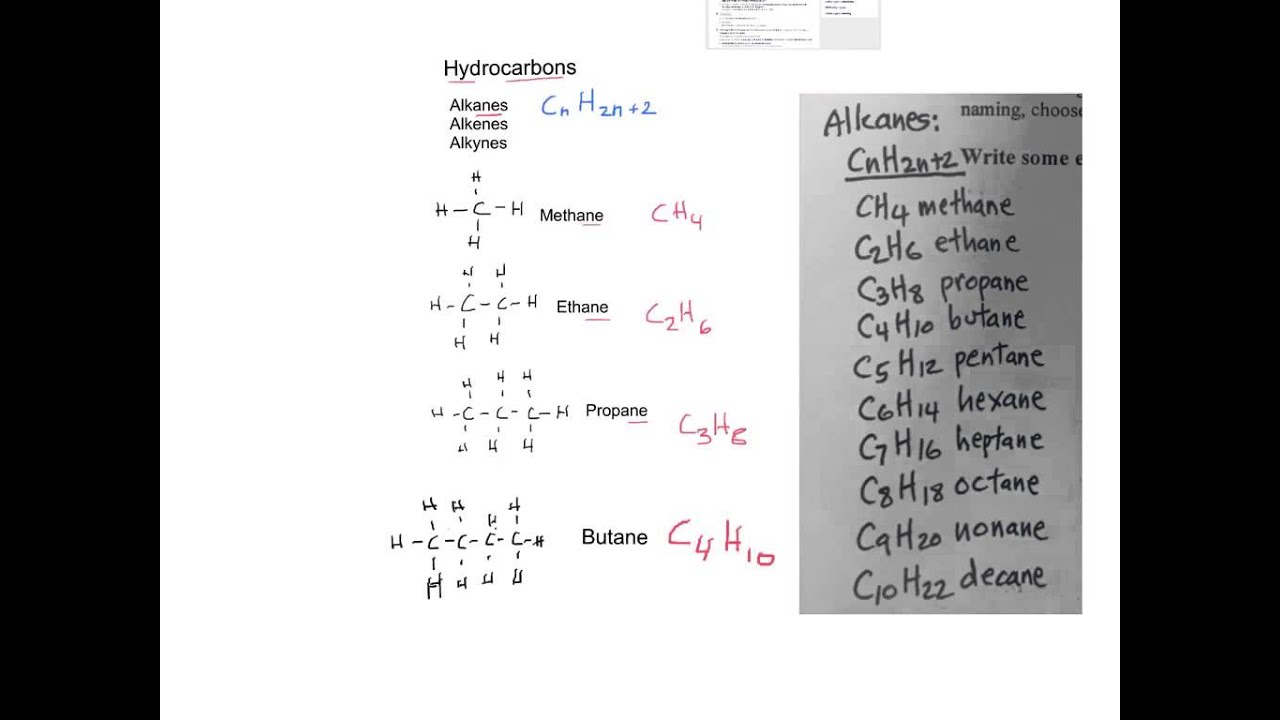
C x n h 2 n + 2. The longest continuous chain should include both the carbon atoms of the triple bond. We will review their nomenclature, and also learn about the vast possibility of reactions using alkenes and alkynes as starting materials. Methane gas is the first member of the homologous series of alkanes. 10) provide the structure of.

We will review their nomenclature, and also learn about the vast possibility of reactions using alkenes and alkynes as starting materials. Introduction to alkenes and alkynes! In an alkane, all 4 4 4 valencies of the carbon atom are satisfied with other hydrogen atoms. Alkene as it had a double bond that can be brocken and new atoms can be.

Alkynes are similar to alkenes in both physical and chemical properties. To make them react further we need to introduce some functional group and the best way is to add halogen. Alkynes are unsaturated carbon that shares a triple bond at the carbon site. First member is ethyne c 2 h 2. About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers.

The addition of halogens in alkenes result in the making of organic salts. In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density! About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features press copyright contact us creators. This means that.

C x n h 2 n + 2. Halogenation goes via free radical mechanism and thus lot of unwanted products + other isomers can be formed. The alkanes are also called as paraffins. About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features press copyright contact us creators. This means that.

Alkynes are unsaturated carbon that shares a double bond at the carbon site. Alkene as it had a double bond that can be brocken and new atoms can be added to the molecule. Alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes are all organic hydrocarbons. Alkynes are unsaturated carbon that shares a triple bond at the carbon site. 2.3 reactions of alkenes and alkynes.